Read Sharp AL-1456 (serv.man7) Service Manual online
AL-1555 COPY PROCESS 6 - 1
[6] COPY PROCESS
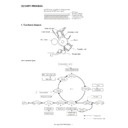
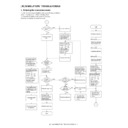
1. Functional diagram
(Basic operation cycle)
(20 microns thick)
Aluminum drum
Pigment layer (0.2
to 0.3 microns thick)
to 0.3 microns thick)
An OPC drum is used for the photoconductor.
(Structure of the OPC drum layers)
(Structure of the OPC drum layers)
OPC layer
Main charger
Laser beam
MG roller
Cleaning blade
Drum
Transfer unit
Resist roller
Exposure
Main high voltage unit
Saw tooth
Charge
Drum
Cleaning
Cleaning blade
Waste toner box
Paper release
Fusing
Separation
Heat roller
Heater lamp
Transfer
Transfer charger
Transfer high
voltage unit
voltage unit
Developing
Toner
Developer
Print process
Paper transport route
Semiconductor laser
Manual feed
PS roller
Focus correction lens
Electrode
Synchronization
with drum
Cassette
paper feed
To face
down tray
down tray
AL-1555 COPY PROCESS 6 - 2
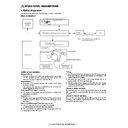
2. Outline of print process
This printer is a non-impact printer that uses a semiconductor laser
and electrostatic print process. This printer uses an OPC (Organic
Photo Conductor) for its photoconductive material.
Photo Conductor) for its photoconductive material.
First, voltage from the main corona unit charges the drum surface and
a latent image is formed on the drum surface using a laser beam. This
latent image forms a visible image on the drum surface when toner is
latent image forms a visible image on the drum surface when toner is
applied. The toner image is then transferred onto the print paper by the
transfer corona and fused on the print paper in the fusing section with
a combination of heat and pressure.
a combination of heat and pressure.
Step-1: Charge
Step-2: Exposure
Step-2: Exposure
*
Latent image is formed on the drum.
Step-3: Developing
Latent image formed on the drum is then changed into visible
image with toner.
Step-4: Transfer
The visible image (toner image) on the drum is transferred
onto the print paper.
Step-5: Cleaning
Residual toner on the drum surface is removed and collected
by the cleaning blade.
Step-6: Optical discharge
Residual charge on the drum surface is removed, by
semiconductor laser beam.
3. Actual print process
Step-1: DC charge
A uniform negative charge is applied over the OPC drum surface by
the main charging unit. Stable potential is maintained by means of the
Scorotron charger.
Scorotron charger.
Positive charges are generated in the aluminum layer.
Step-2: Exposure (laser beam, lens)
A Laser beam is generated from the semiconductor laser and
controlled by the print pattern signal. The laser writes onto the OPC
controlled by the print pattern signal. The laser writes onto the OPC
drum surface through the polygon mirrors and lens. The resistance of
the OPC layer decreases for an area exposed by the laser beam
(corresponding to the print pattern signal). The beam neutralizes the
(corresponding to the print pattern signal). The beam neutralizes the
negative charge. An electrostatic latent image is formed on the drum
surface.
About
DC5.5KV
( 580V/ 390V)
OPC layer
Pigment
layer
layer
Aluminum
drum
drum
OPC layer
Pigment
layer
layer
Aluminum
layer
layer
Drum surface charge
after the exposure
after the exposure
Non-image area
Image area
Semiconductor laser
Exposure
(semiconductor laser)
(semiconductor laser)
AL-1555 COPY PROCESS 6 - 3
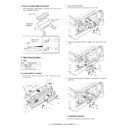
Step-3: Developing (DC bias)
A bias potential is applied to the MG roller in the two component
magnetic brush developing method, and the toner is charged negative
magnetic brush developing method, and the toner is charged negative
through friction with the carrier.
Non-image area of the drum surface charged with negative potential
repel the toner, whereas the laser exposed portions where no negative
repel the toner, whereas the laser exposed portions where no negative
charges exist, attract the toner. As a result, a visible image appears on
the drum surface.
Toner is attracted over the shadowed area because of the developing
bias.
Step-4: Transfer
The visible image on the drum surface is transferred onto the print
paper by applying a positive charge from the transfer corona to the
paper by applying a positive charge from the transfer corona to the
backside of the print paper.
Step-5: Separation
Since the print paper is charged positively by the transfer corona, it is
discharged by the separation corona. The separation corona is
connected to ground.
connected to ground.
Step-6: Cleaning
Toner remaining on the drum is removed and collected by the cleaning
blade. It is transported to the waste toner collecting section in the
blade. It is transported to the waste toner collecting section in the
cleaning unit by the waste toner transport roller.
S
N
N
:Carrier (Magnetized particle)
:Toner (Charge negative by friction)
(N) (S) Permanent magnet
:Toner (Charge negative by friction)
(N) (S) Permanent magnet
(provided in three locations)
MG roller
DC
400V 8V
About DC 5.2kV
AL-1555 COPY PROCESS 6 - 4
Step-7: Optical discharge (Semiconductor laser)
Before the drum rotation is stopped, the semiconductor laser is
radiated onto the drum to reduce the electrical resistance in the OPC
radiated onto the drum to reduce the electrical resistance in the OPC
layer and eliminate residual charge, providing a uniform state to the
drum surface for the next page to be printed.
When the electrical resistance is reduced, positive charges on the
When the electrical resistance is reduced, positive charges on the
aluminum layer are moved and neutralized with negative charges on
the OPC layer.
Charge by the Scorotron charger
Function
The Scorotron charger functions to maintain uniform surface potential
on the drum at all times, It control the surface potential regardless of
on the drum at all times, It control the surface potential regardless of
the charge characteristics of the photoconductor.
Basic function
A screen grid is placed between the saw tooth and the
photoconductor. A stable voltage is added to the screen grid to
maintain the corona current on the photoconductor.
As the photoconductor is charged by the saw tooth from the main
As the photoconductor is charged by the saw tooth from the main
corona unit, the surface potential increases. This increases the current
flowing through the screen grid. When the photoconductor potential
nears the grid potential, the current turns to flow to the grid so that the
nears the grid potential, the current turns to flow to the grid so that the
photoconductor potential can be maintained at a stable level.
Process controlling
Function
The print pattern signal is converted into an invisible image by the
semiconductor laser using negative to positive (reversible) developing
semiconductor laser using negative to positive (reversible) developing
method. Therefore, if the developing bias is added before the drum is
charged, toner is attracted onto the drum. If the developing bias is not
added when the drum is charged, the carrier is attracted to the drum
added when the drum is charged, the carrier is attracted to the drum
because of the strong electrostatic force of the drum.
To avoid this, the process is controlled by adjusting the drum potential
and the grid potential of the Scorotron charger.
and the grid potential of the Scorotron charger.
Basic function
Voltage added to the screen grid can be selected, high and low. To
make it easily understood, the figure below shows voltage transition at
make it easily understood, the figure below shows voltage transition at
the developer unit.
Start
1) Because the grid potential is at a low level, the drum potential is at
about -400V. (Carrier may not be attracted though the carrier is
pulled towards the drum by the electrostatic force of -400V.
pulled towards the drum by the electrostatic force of -400V.
2) Developing bias (-400V) is applied when the photoconductor
potential is switched from LOW to HIGH.
3) Once developing bias (-400V) is applied and the photo conductor
potential rises to HIGH, toner will not be attracted to the drum.
Stop
The reverse sequence takes place.
Retaining developing bias at an abnormal occurrence
Retaining developing bias at an abnormal occurrence
Function
The developing bias will be lost if the power supply was removed
during print process. In this event, the drum potential slightly abates
during print process. In this event, the drum potential slightly abates
and the carrier makes deposits on the drum because of strong static
power. To prevent this, the machine incorporates a function to retain
the developing bias for a certain period and decrease the voltage
the developing bias for a certain period and decrease the voltage
gradually against possible power loss.
Basic function
Normally, the developing bias voltage is retained for a certain time
before the drum comes to a complete stop if the machine should stop
before completing the normal print cycle. The developing bias can be
added before resuming the operation after an abnormal interruption.
added before resuming the operation after an abnormal interruption.
Therefore, carrier will not make a deposit on the drum surface.
Semiconductor laser
0
START
STOP
Print potential
Toner attract
potential
potential
2)
3)
1)
Low
4)
High
Drum potential
Developing bias
Time